Concept
For the preparation and implementation of an excursion, in which a field experiment with mobile GIS support is to be integrated, the excursion leader, the lecturer and the GIS group of the Department of Environmental Systems Sciences (D-USYS) worked closely together.
The following figure schematically links the sequence of the individual phases with the didactic workflow and the technical architecture of a GISsmox excursion.
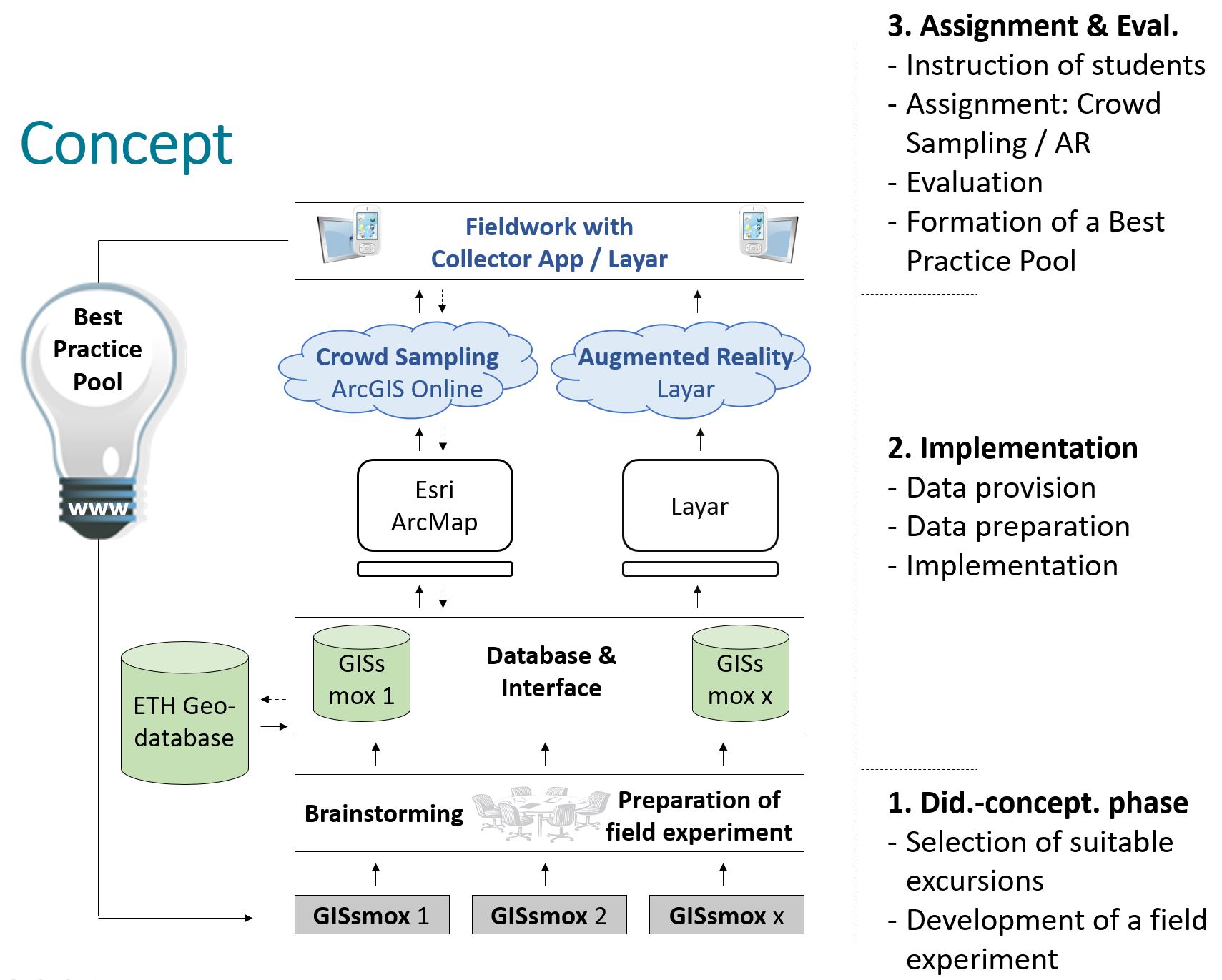
1. Didactic-conceptual Phase:
The planning of each excursion begins with a didactic-conceptual phase in which the lecturer works out an initial scenario together with the excursion leader. This involves checking the extent to which the use of mobile devices can create didactic added value for this excursion and which data should be recorded in the field. Based on this, the practical and technical feasibility will be checked together with the GIS group and any necessary adjustments will be made. In addition, it will be clarified whether further instruments or permits are necessary for the collection of the data.
2. Implementation:
This is followed by the implementation of the data structure by those responsible for GIS at the D-USYS, based on the Esri software ArcGIS Desktop. Furthermore, it is defined how the data to be recorded is to be visually displayed and processed after acquisition. As soon as this work is completed, the data will be integrated into the cloud-based content management system external external page ArcGIS Online by Esri and made accessible to the students with the help of the Collector for ArcGIS App (iOS, Android & Windows Phone) or external external page ArcGIS Field Maps.
3. Deployment and Evaluation
Phase 1: Data Collection / Crowd Sampling Phase
Before each Integrated Field Trip, students receive information materials to prepare themselves. For a GISsmox field trip, participants are additionally informed that they will be recording data using their smartphones and tablets. Students are asked to download the freely available Field Maps (formerly: Collector for ArcGIS) in advance.
Phase 2: Data Collection / Crowd Sampling
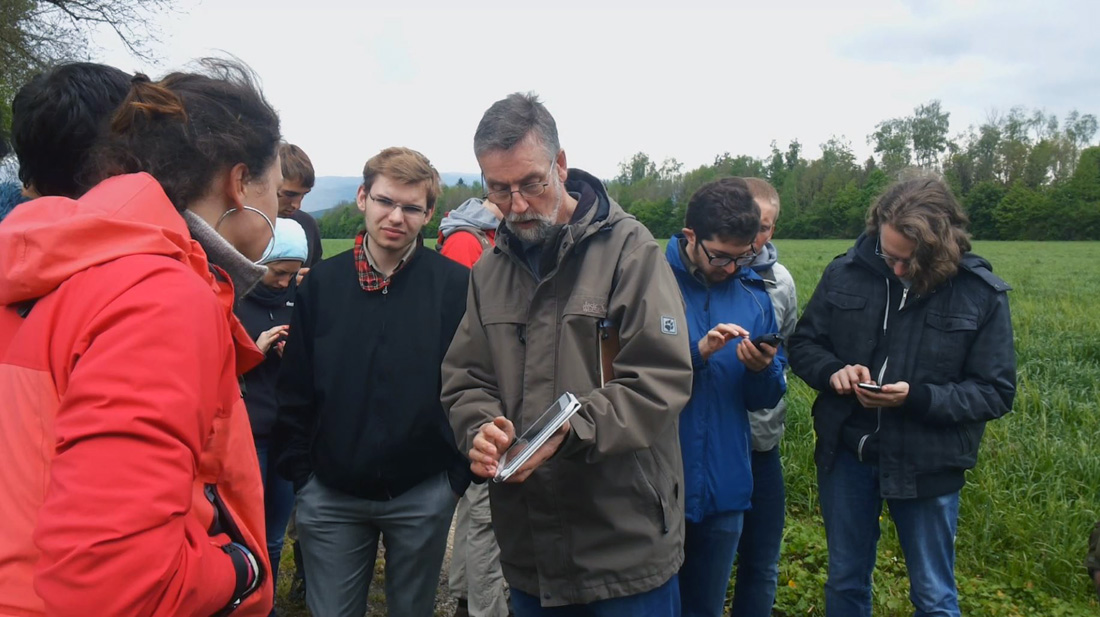
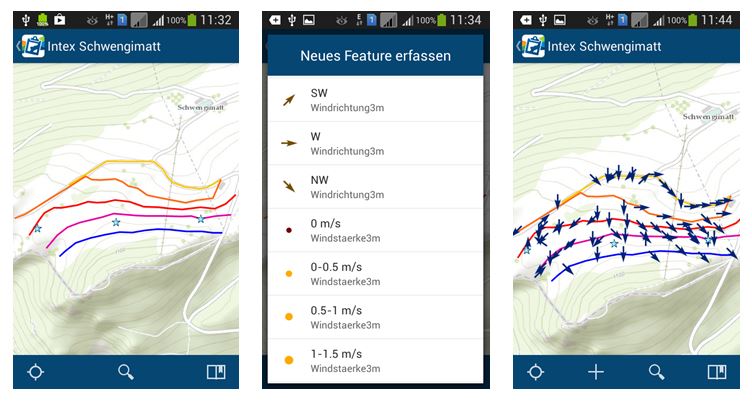
Data collection is usually done in groups of two. This way, the students can consult with each other during data collection and entry, e.g. if there are measurement uncertainties. While the students enter the required data via a mask, the GPS receivers of the devices provide the exact position for the recorded data points.
All participants can see in real time where others have recorded something and what properties the recorded objects have. In this way, a data picture of the investigated area is already created during the collection phase and initial hypotheses can be formed and discussed in the collection teams (see figure below).
Phase 3: Evaluation
Immediately after the data collection, the students meet and discuss or analyse the results together based on the prepared questions in groups and in plenary with the experts. The optimal didactic design of this evaluation phase is one of the core objectives of the GISsmox project.

Phase 4: Evaluation
After each excursion, an evaluation should be carried out with regard to the didactic added value and the acceptance of the new medium. For this purpose, the opinions and views of both the students and the excursion leader will be gathered. Information from direct conversations and observations during the excursion will also be included in the evaluation. Technical aspects will also be taken into account.
Phase 5: Post processing
The data collected by the students is stored in a geodatabase by the GIS group and can thus be reused next year. This means that in future GISsmox excursions can take into account not only the spatial aspect but also the temporal aspect.